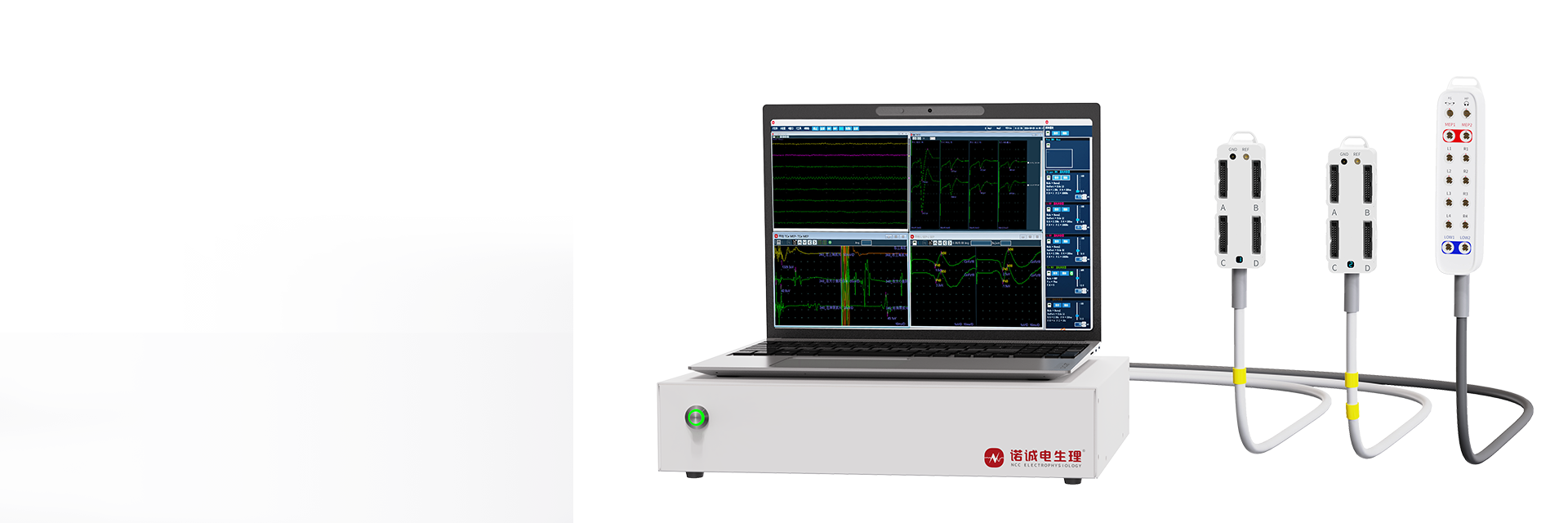
● 16/32 channels amplifier with 1 extra low current stimulation port, 9 channels stimulation box;
● 16 flexible measurement modalities such as EMG, MEP, SEP, BAEP, VEP, EEG, TOF and Pedicle screw are available to meet the different surgical requirements of spinal, neurosurgery and ENT.
● Equipped with integrated consumables, which possess a robust anti-interference capability, and enhances the accuracy of waveform.
● The entire system is connected by a single wire, which reduces error rates and improves efficiency. Save the time required for preoperative preparation.
● Minimize the wear and tear of the device.
● Dual screens are adjustable: a main screen and an extended screen,and the back-to-back mode allows surgeons to view monitoring results directly. The system is also compatible with an external microscope for more precise monitoring.
● Designed as a portable suitcase, all accessories can be stored in one suitcase.
● Convenient for transportation between hospitals.
● Flexible configuration of trolleys to meet various usage scenarios.
 390Electrical safety monitoring
390Electrical safety monitoring 101Performance indicator testing
101Performance indicator testing 4919Software testing and detection
4919Software testing and detection 14Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing
14Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing 6Biocompatibility testing
6Biocompatibility testing 8Simulated transportation test
8Simulated transportation test

| Department | Surgeries | The main risks and effects |
|---|---|---|
| Orthopedics | Cervical spine surgery | Spinal cord injury (high paraplegia) Nerve root injury (poor postoperative recovery) Safety of screw implantation |
| Thoracolumbar spine surgery | Spinal cord injury (risk of paralysis below the brachial plexus, with impairment of urination and excrement function) Nerve root injury (poor postoperative recovery) Safety of screw implantation | |
| Coccyx surgery | Spinal cord injury (risk of paralysis below the brachial plexus, with impairment of urination and excrement function) Nerve root injury (poor postoperative recovery) Safety of screw implantation | |
| Thoracolumbar spine surgery | Spinal cord injury (high paraplegia) Nerve root injury (poor postoperative recovery) Safety of screw implantation | |
| Neurosurgery | Microvasc | Facial nerve damage |
| ular decompression | Brainstem injury Surgical terminus determination | |
| Hypophysoma | Optic nerve injury Monitoring visual evoked potentials | |
| Carotid endarterectomy | Irreversible motor dysfunction caused by ischemia Monitoring vascular perfusion | |
| Cerebellar pontine area | Facial nerve damage (facial paralysis) Acoustic nerve injury (hearing loss) Exploration and confirmation of the facial nerve | |
| Functional area tumor | Motor dysfunction Aphasia Localization of functional areas | |
| Arterial aneurysm | Irreversible motor dysfunction caused by ischemia Monitoring vascular perfusion | |
| Intramedullary tumor | Spinal cord conduction dysfunction (motor, sensory) Spinal nerve roots injury Monitoring screw implantation |
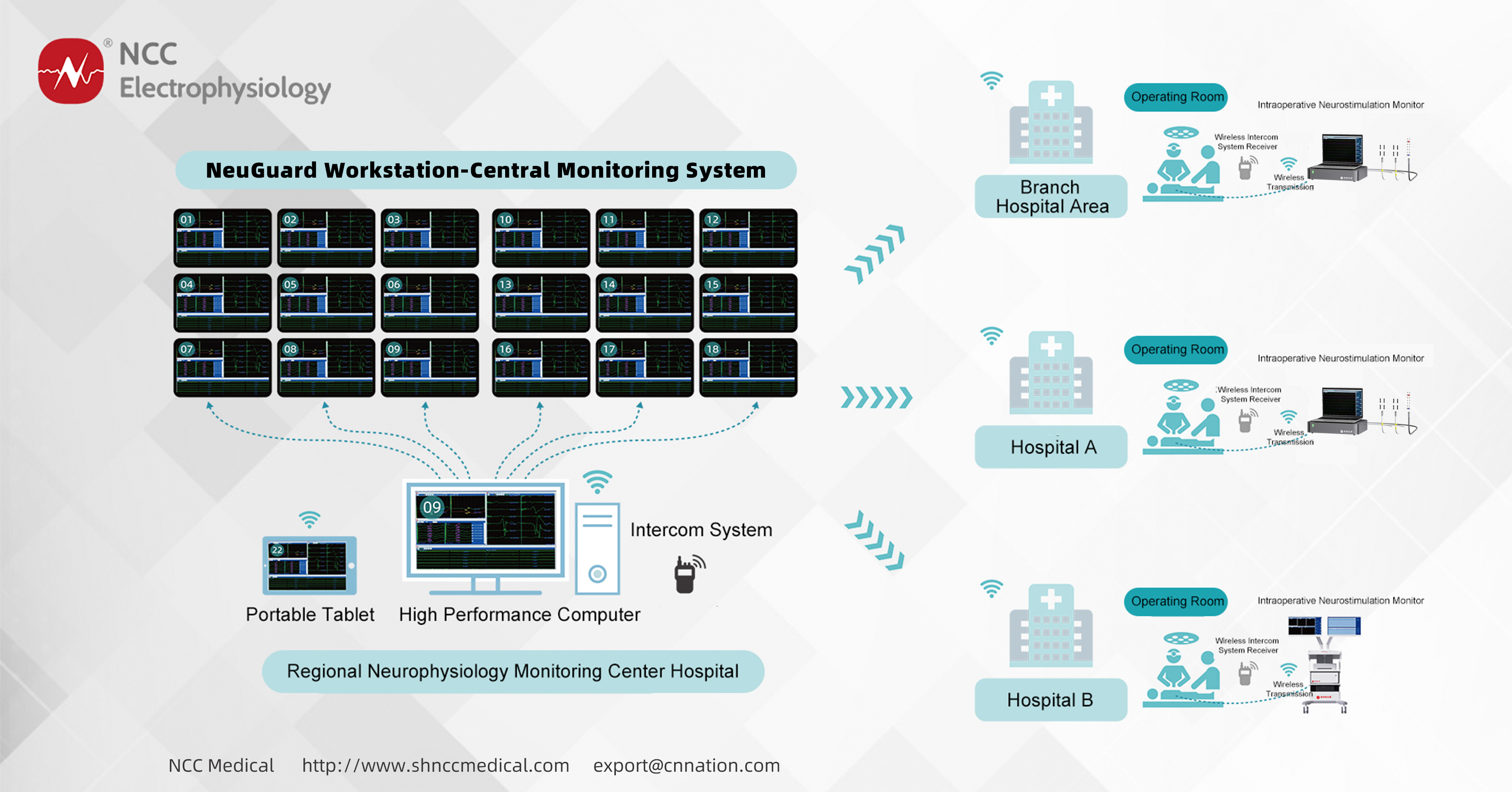
NeuGuard Workstation-central Monitoring system

Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring Solutions
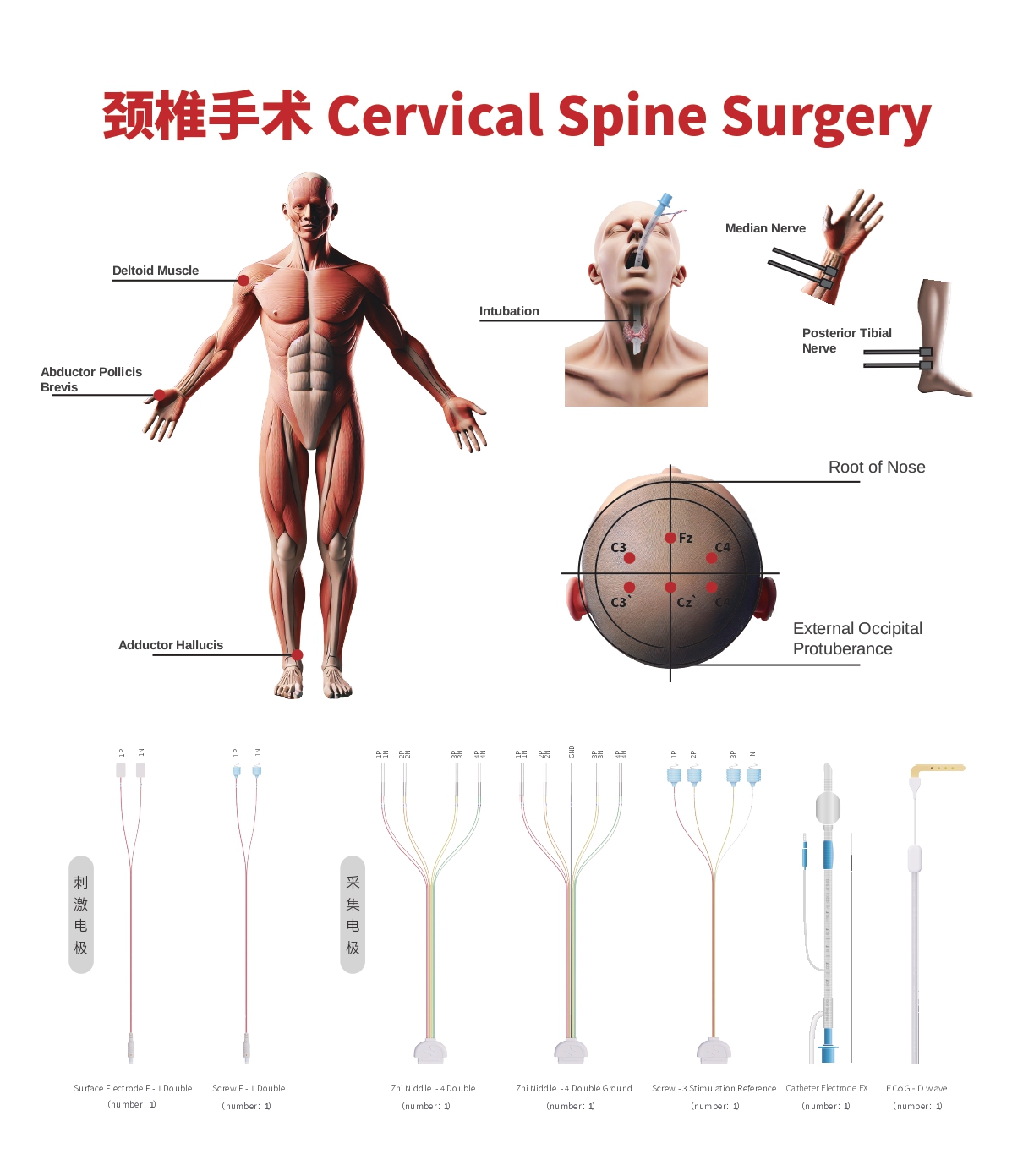
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the ascending spinal pathways to protect the patient's sensory function.
- Stimulating Site: Median nerve or ulnar nerve (upper limbs), posterior tibial nerve (lower limbs).
- Recording Site: C3’-Fz, C4’-Fz (upper limbs), Cz-Fz (lower limbs).
Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potential (TCe MEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the descending spinal pathways to assess and evaluate the patient's swallowing and motor function.
- Stimulating Site: C3, C4 or C1, C2 (precentral gyrus).
- Recording Site: Vocal cords (intubation electrodes), deltoid, abductor pollicis brevis, adductor hallucis, etc.
Free-run Electromyography (Free EMG)
- Observes real-time nerve traction responses.
Train-of-Four (TOF) Test
- Immediate monitoring of the patient's neuromuscular blockade status.
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the ascending spinal pathways to protect the patient's sensory function.
- Stimulating Site: Posterior tibial nerve (lower limbs).
- Recording Site: Cz-Fz (lower limbs).
Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potential (TCe MEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the descending spinal pathways to assess and evaluate the patient's motor function.
- Stimulating Site: C3, C4 or C1, C2 (precentral gyrus).
- Recording Site: Abductor pollicis brevis, adductor muscles, rectus femoris, tibialis anterior, abductor hallucis.
Free-run Electromyography (Free EMG)
- Observes real-time nerve traction responses.
Pedicle Screw Testing
- Automatically detects the accuracy of each screw placement.
Train-of-Four (TOF) Test
- Immediate monitoring of the patient's neuromuscular blockade status.
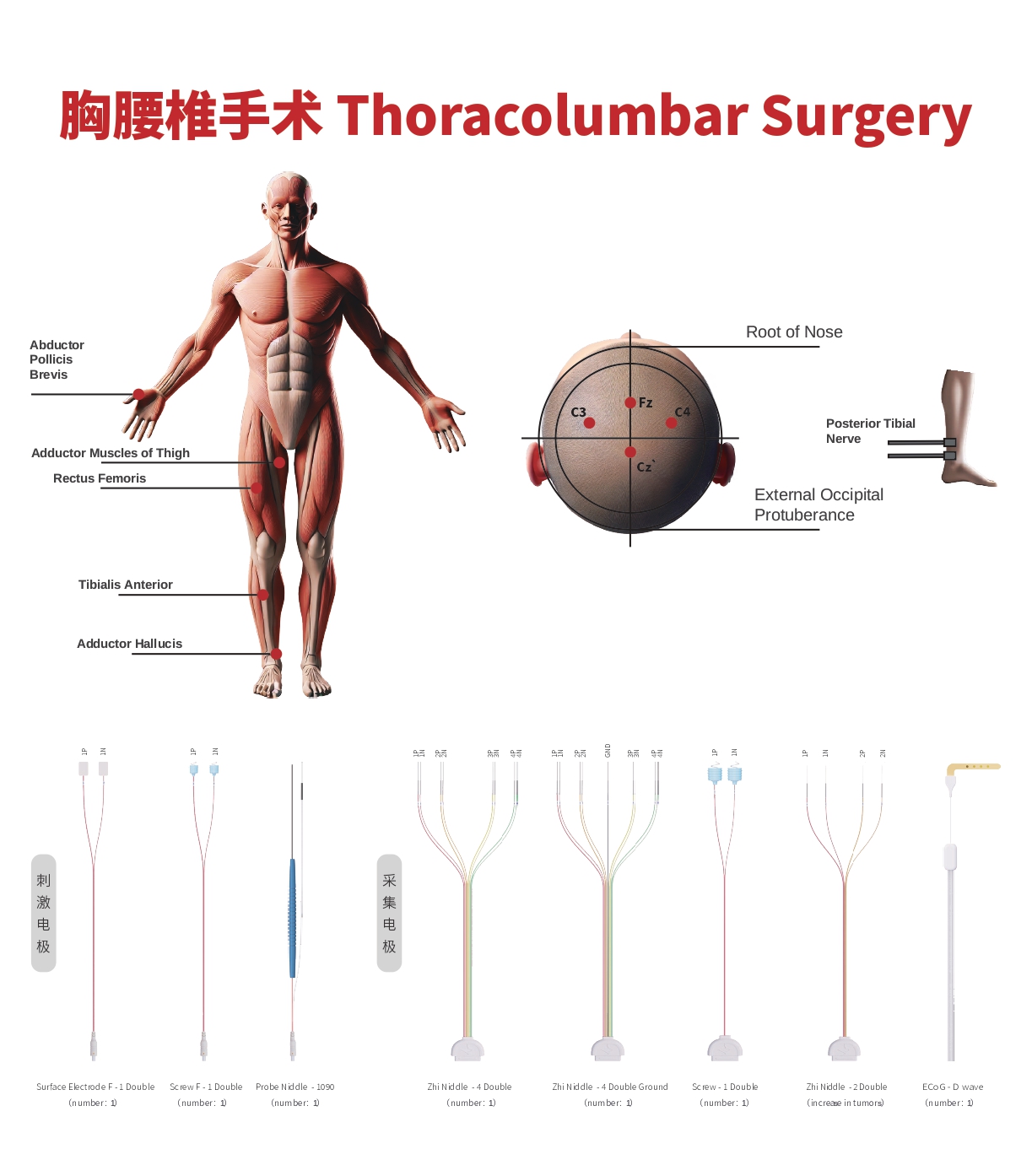
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the ascending spinal pathways to protect the patient's sensory function.
- Stimulating Site: Median nerve or ulnar nerve (upper limbs), posterior tibial nerve (lower limbs).
- Recording Site: C3’-Fz, C4’-Fz (upper limbs), Cz-Fz (lower limbs).
Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potential (TCe MEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the descending spinal pathways to assess and evaluate the patient's motor function.
- Stimulating Site: C3, C4 or C1, C2 (precentral gyrus).
- Recording Site: Abductor pollicis brevis, rectus abdominis, adductor muscles, rectus femoris, tibialis anterior, abductor hallucis, anal sphincter.
Free-run Electromyography (Free EMG)
- Observes real-time nerve traction responses.
Pedicle Screw Testing
- Automatically detects the accuracy of each screw placement.
Train-of-Four (TOF) Test
- Immediate monitoring of the patient's neuromuscular blockade status.
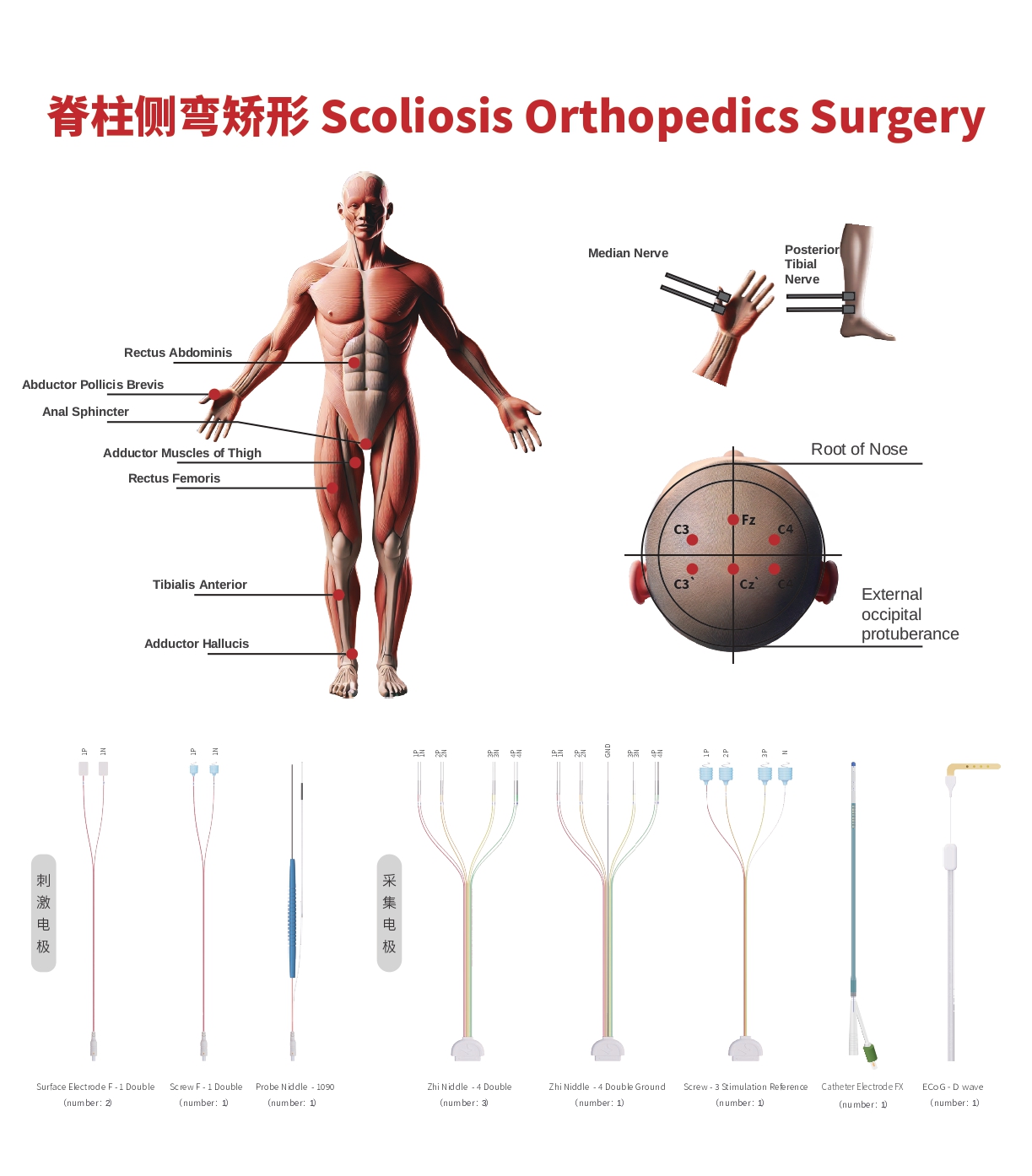
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the ascending spinal pathways to protect the patient's sensory function.
- Stimulating Site: Posterior tibial nerve (lower limbs).
- Recording Site: Cz-Fz (lower limbs).
Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potential (TCe MEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the descending spinal pathways to assess and evaluate the patient's motor function.
- Stimulating Site: C3, C4 or C1, C2 (precentral gyrus).
- Recording Site: Abductor pollicis brevis, adductor muscles, rectus femoris, tibialis anterior, abductor hallucis, anal sphincter.
Triggered Electromyography (Trigger EMG)
- Identifies and differentiates nerves from unknown tissues.
Free-run Electromyography (Free EMG)
- Observes real-time nerve traction responses.
Bulbocavernosus Reflex (BCR) Monitoring
- Immediate monitoring of the patient's sacral nerve reflex.
Train-of-Four (TOF) Test
- Immediate monitoring of the patient's neuromuscular blockade status.
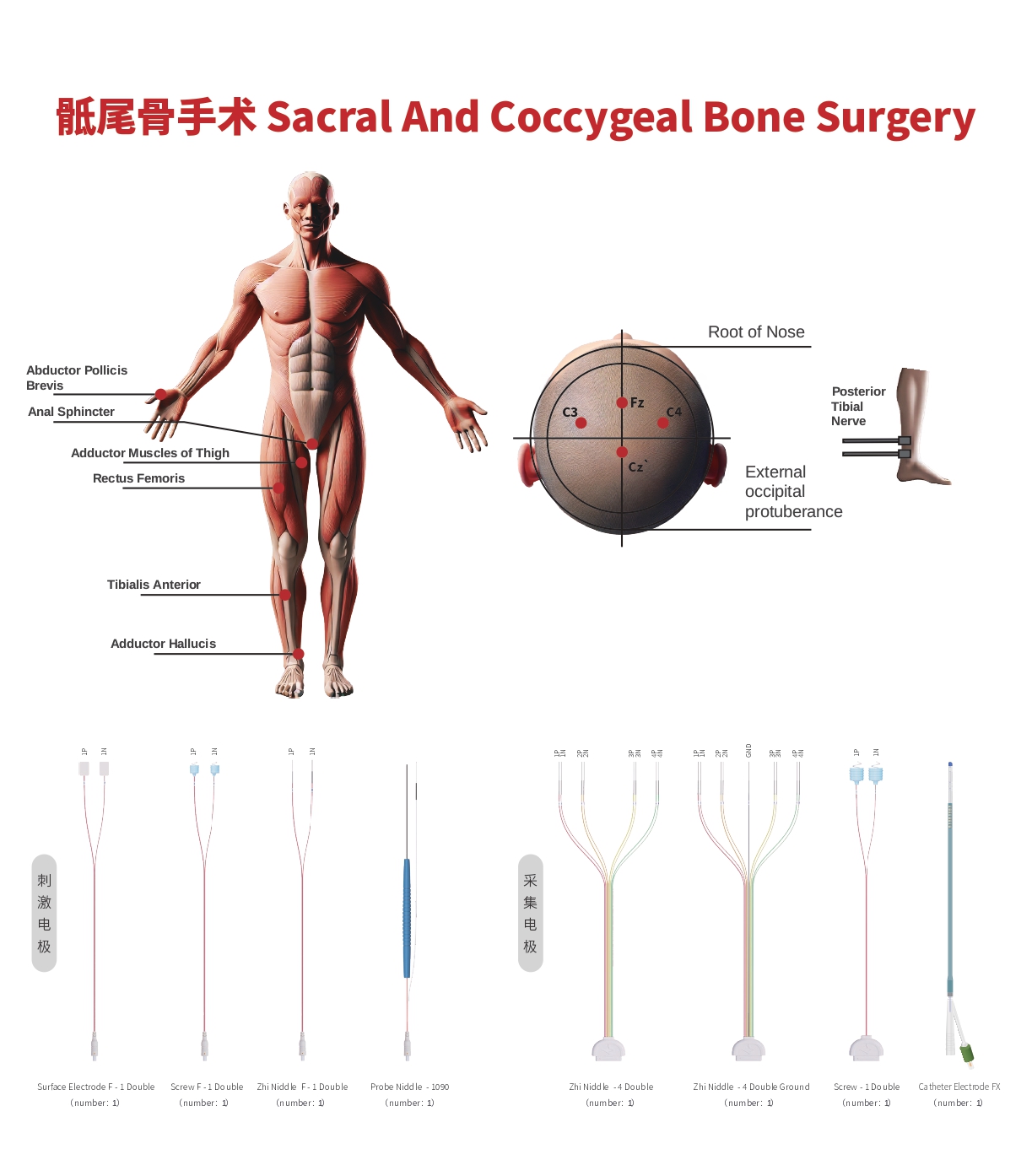
Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV)
- Nerve conduction velocity is a diagnostic technique used to evaluate the conduction function of peripheral nerves, typically including motor nerve conduction velocity (MCV) and sensory nerve conduction velocity (SCV).
- Abnormalities in MCV and SCV are manifested as slowed conduction velocity and reduced amplitude. NCV measurement can be used to identify and differentiate peripheral nerves during surgery.
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the ascending pathways to protect the patient's sensory function.
- Stimulating Site: Median nerve or ulnar nerve (upper limbs), posterior tibial nerve (lower limbs).
- Recording Site: C3’-Fz, C4’-Fz (upper limbs), Cz-Fz (lower limbs).
Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potential (TCe MEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the descending pathways to assess and evaluate the patient's motor function.
- Stimulating Site: C3, C4 or C1, C2 (precentral gyrus).
- Recording Site: Corresponding muscles of the surgical limb.
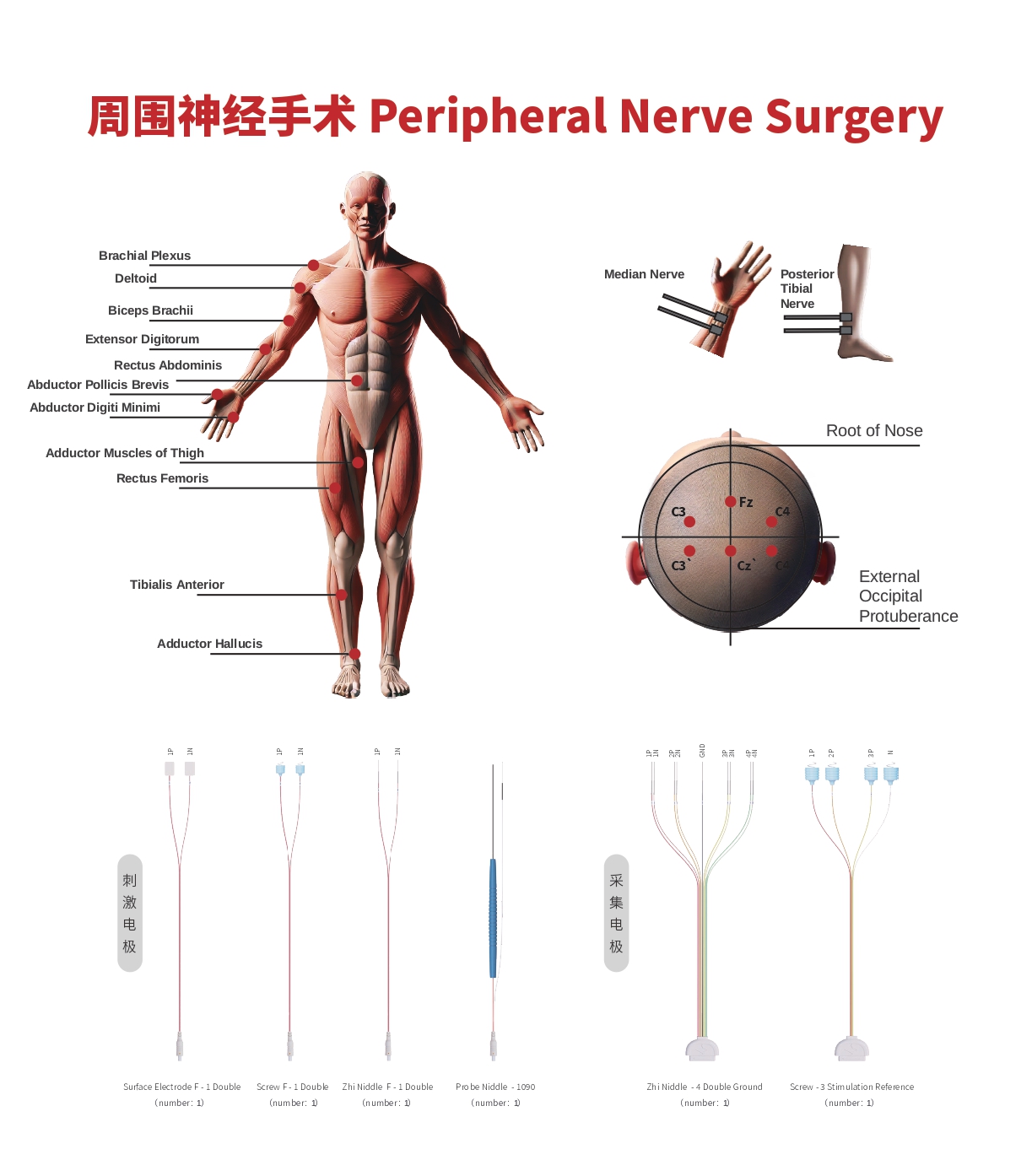
Lateral Spread Response (LSR)
- Recording Site:
- 1. Frontalis muscle
- 2. Orbicularis oculi muscle
- 3. Orbicularis oris muscle
- 4. Mentalis muscle
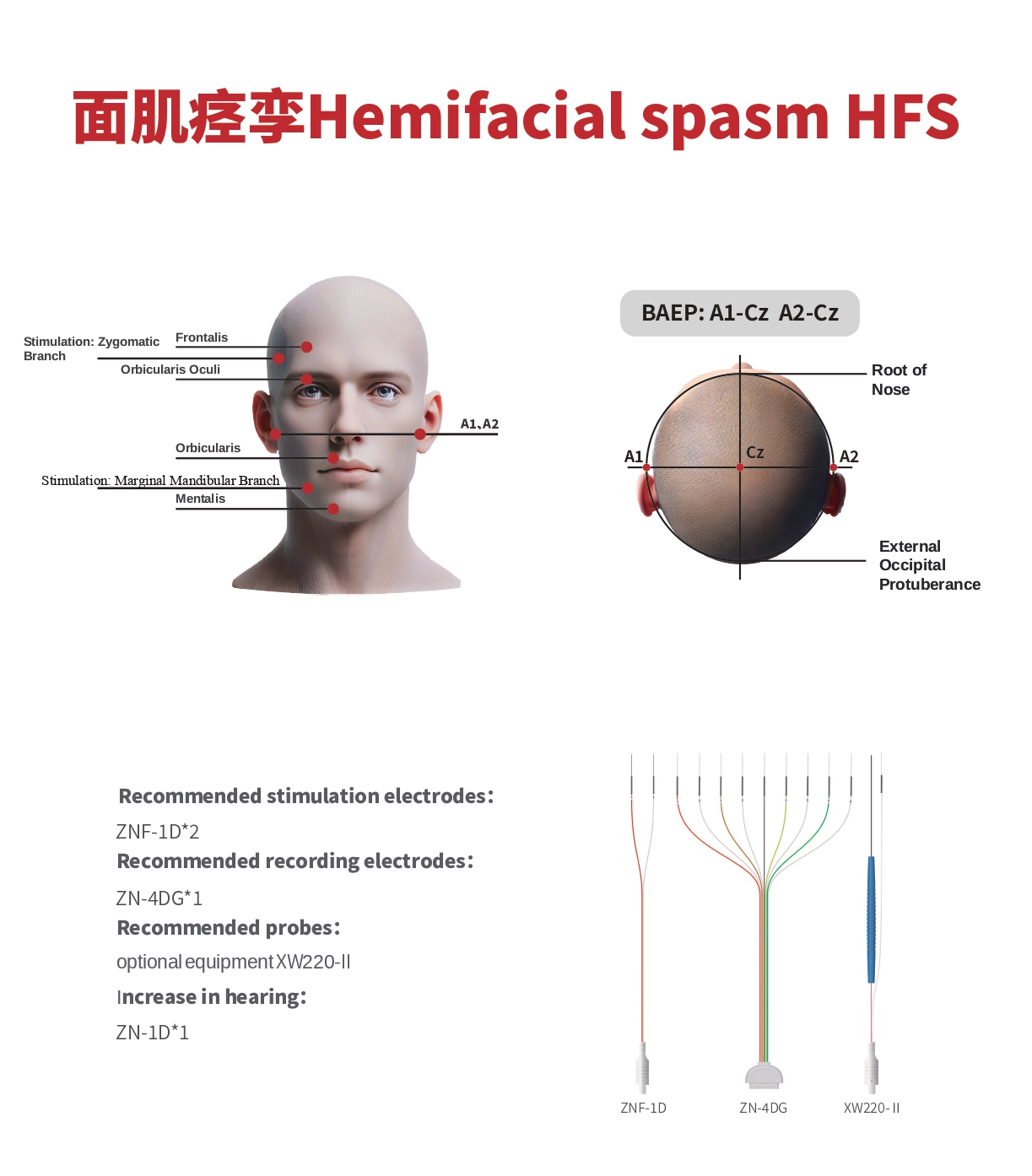
Stimulation Sites:
- Scheme 1: Mandibular branch - Orbicularis oculi muscle:
- Stimulation Site: Mandibular branch of the facial nerve (at the angle of the mandible)
- Scheme 2: Zygomatic branch - Mentalis muscle:
- Stimulation Site: Zygomatic branch of the facial nerve (at the midpoint along the line connecting the zygomatic arch and the tragus)
Recommended Stimulation Electrode:
- ZNF-1D*2
- Recommended Recording Electrode:
- ZN-4DG*1
- Recommended Probe:
- Optional XW220-Ⅱ
- Auditory Enhancement:
- ZN-1D*1
Free EMG
- Monitors traction responses of the Trigeminal Nerve (V), Facial Nerve (VII), Vagus Nerve (X), Accessory Nerve (XI), and Hypoglossal Nerve (XII).
Trigger EMG
- Electrical stimulation of the Trigeminal Nerve and Facial Nerve is used for locating the Trigeminal Nerve (V) and Facial Nerve (VII).
Facial MEP
- Evaluates the intraoperative function of the facial nerve.
- Stimulation Site: (Precentral gyrus, face motor representation area)
- Recording Sites: Mentalis muscle, Orbicularis oris muscle.
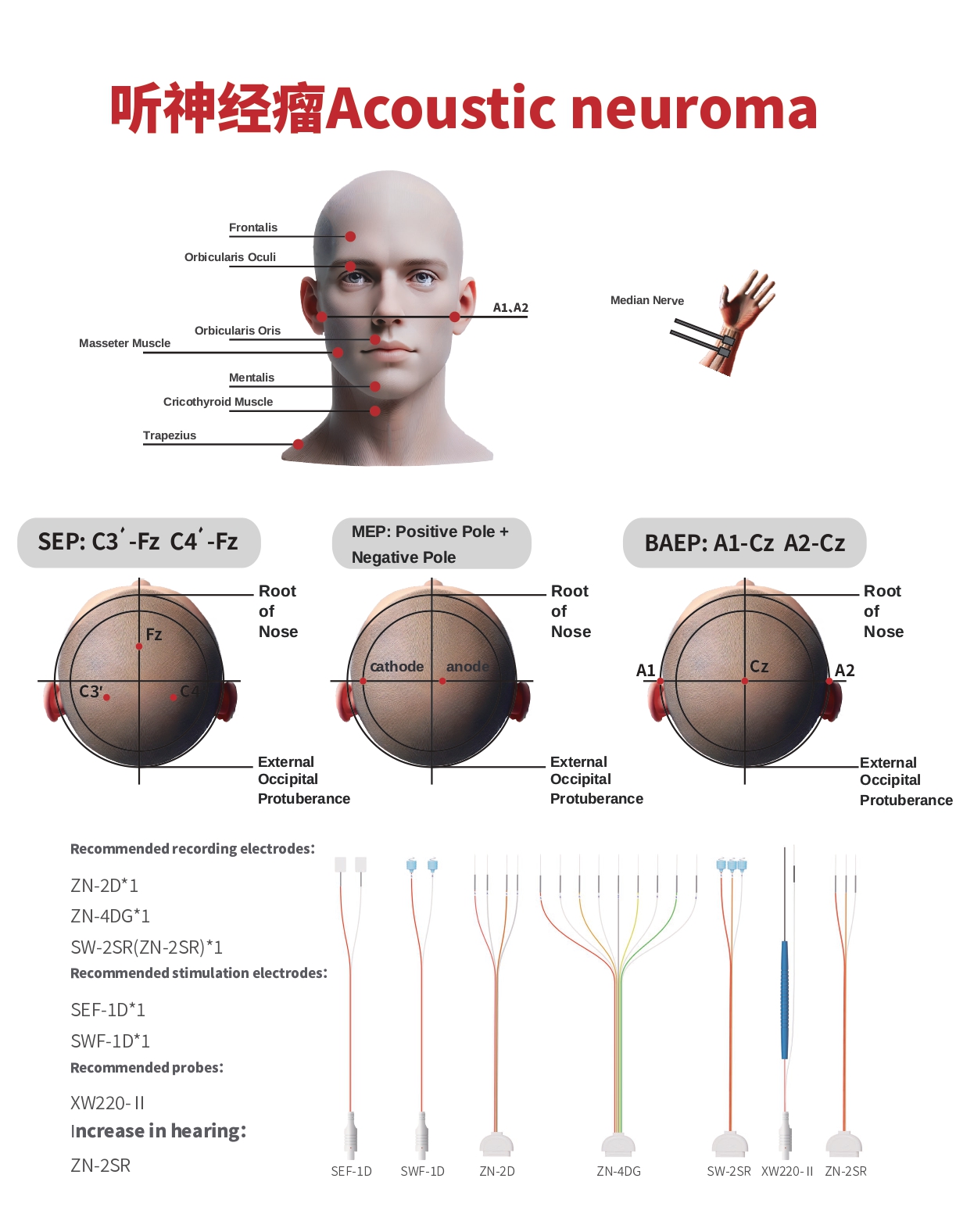
Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potential (BAEP)
- Protects the function of the auditory nerve and brainstem on the affected side.
- Performed on the healthy side (in cases of hearing loss on the affected side) or bilaterally.
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
- Upper Limb Somatosensory Evoked Potential
- Protects the brainstem function on the affected side.
Recommended Stimulation Electrode:
- ZN-2D*1
- ZN-4DG*1
- SW-2SR (ZN-2SR)*1
- Recommended Stimulation Electrodes:
- SEF-1D*1
- SWF-1D*1
- Recommended Probe:
- XW220-Ⅱ
- Auditory Enhancement:
- ZN-2SR
Somatosensory Evoked Potential, SSEP
- Real-time monitoring of the spinal ascending pathways to assess the patient's sensory function.
- Stimulation Sites: Median nerve of the upper limb, posterior tibial nerve of the lower limb
- Recording Sites: C3’-Fz, C4’-Fz for the upper limb; Cz’-Fz for the lower limb
Transcranial Cervical Motor Evoked Potential (TCe MEP)
- Real-time monitoring of the spinal descending pathways to monitor and evaluate the patient's motor function.
- Stimulation Sites: C1, C2 (precentral gyrus)
- Recording Sites: Muscles corresponding to the respective spinal segments
Free EMG (Electromyography): Observes real-time nerve stretch responses.
Trigger EMG: Identifies and differentiates nerves from unidentified tissues.
Automatic Pedicle Screw Monitoring: Automatically detects the accuracy of each screw implantation.
TOF Test (Train-of-Four Test): Monitors the patient's neuromuscular blockade and metabolism in real time.
BCR Monitoring (Bulbocavernosus Reflex Monitoring): Monitors the patient's sacral nerve reflexes in real time.
Recommended Stimulation Electrodes:
- SEF-1D*2
- SWF-1D*1
- Recommended Recording Electrodes:
- ZN-4D*3
- ZN-4DG*1
- SW-3SR (ZN-3SR)*1
- D-wave Electrode*1
- Recommended Probe:
- XW220-Ⅱ
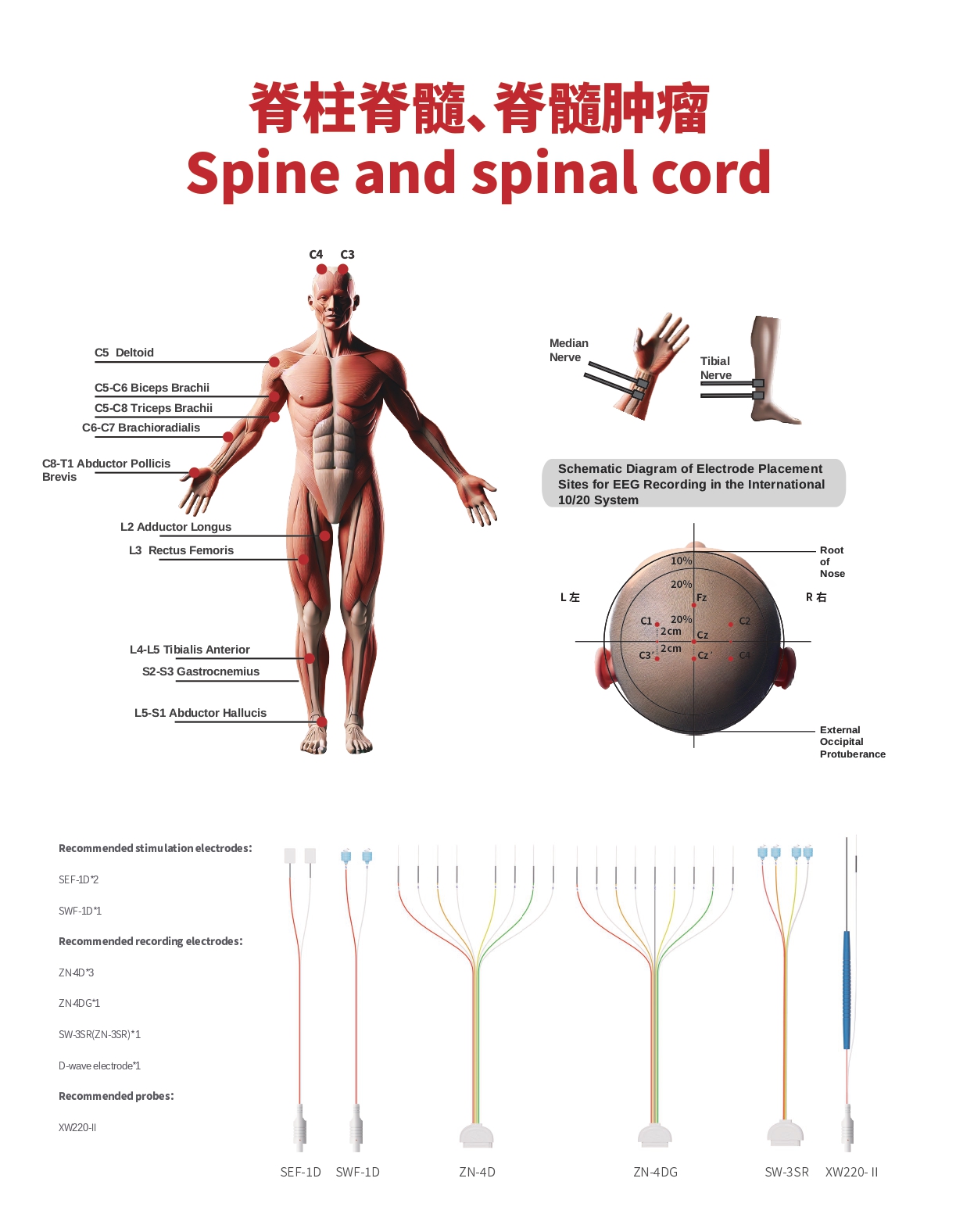
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
- Monitors the afferent sensory/dorsal column to detect changes in sensory function.
- Stimulation Sites: Median nerve of the upper limb, posterior tibial nerve of the lower limb
- Recording Sites: C3’-Fz, C4’-Fz for the upper limb; Cz’-Fz for the lower limb
Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potential (TCeMEP)
- Monitors the lateral corticospinal tract/motor pathway to detect changes caused by mechanical manipulation or vascular ischemia.
- Stimulation Sites: C1/C2 - Primary Motor Cortex
- Recording Sites: Deltoid muscle, Abductor pollicis brevis muscle, Anterior tibialis muscle, Adductor hallucis muscle
Recommended Stimulation Electrodes:
- SEF-1D*2
- SWF-1D
- Recommended Recording Electrodes:
- ZN-4D
- ZN-4DG*1
- SW-3SR (ZN-3SR)*1
- ZN-4S (ZN-4SR)*1
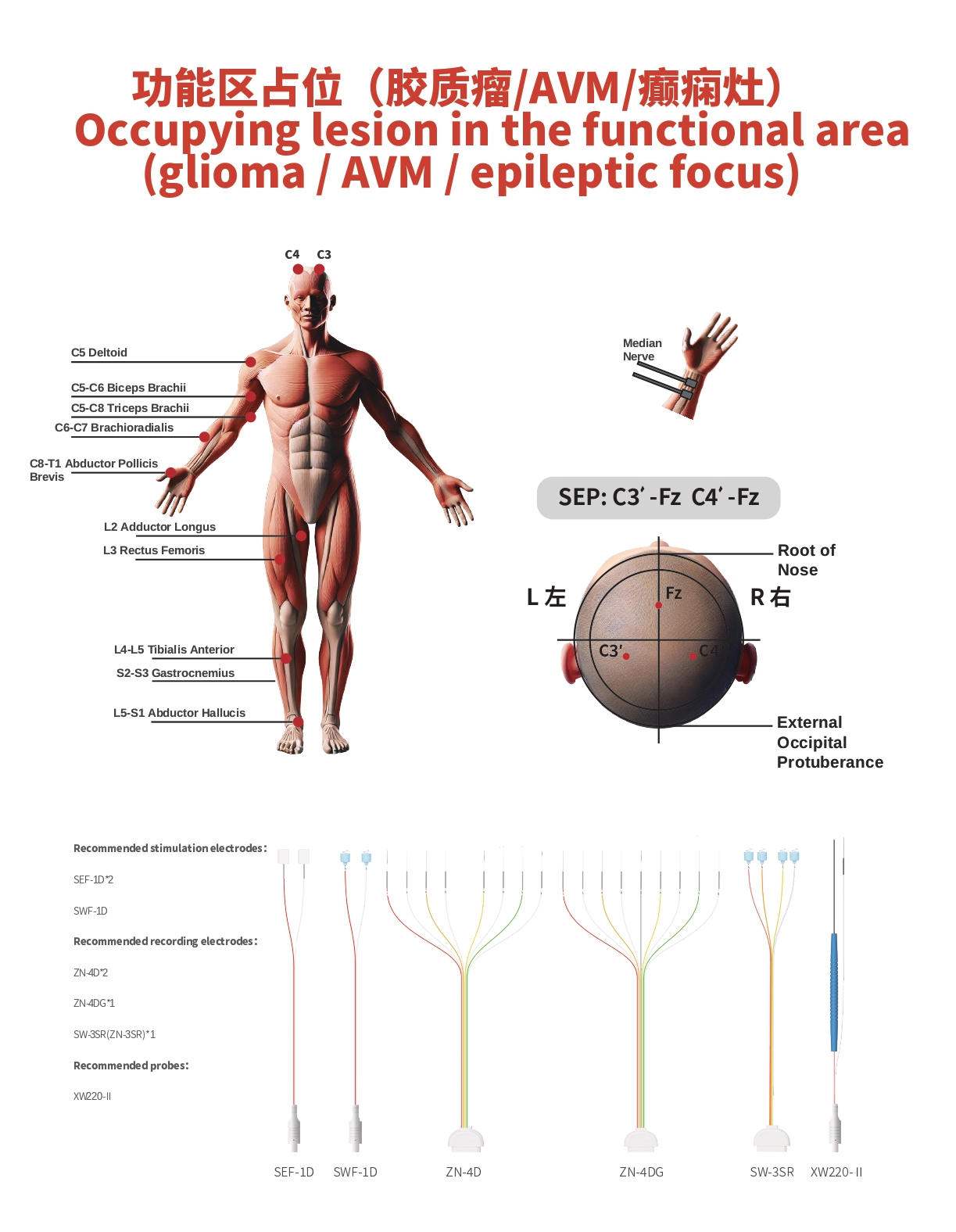
Phase Reversal for Central Sulcus Localization
- Stimulation Site: Contralateral Median Nerve
- Recording Site: Central Sulcus of the Cerebral Cortex
Direct Cortical and Subcortical Electrical Stimulation
- To maximize tumor resection while preserving the integrity of brain functions, it is necessary to intermittently confirm and map the boundaries of functional areas to prevent new-onset hemiplegia and aphasia.
- Recording Sites:
- Face, Trapezius, Deltoid, Extensor Digitorum Communis, Thenar and Hypothenar Muscles, Quadriceps Femoris, Anterior Tibialis, Abductor Pollicis Brevis
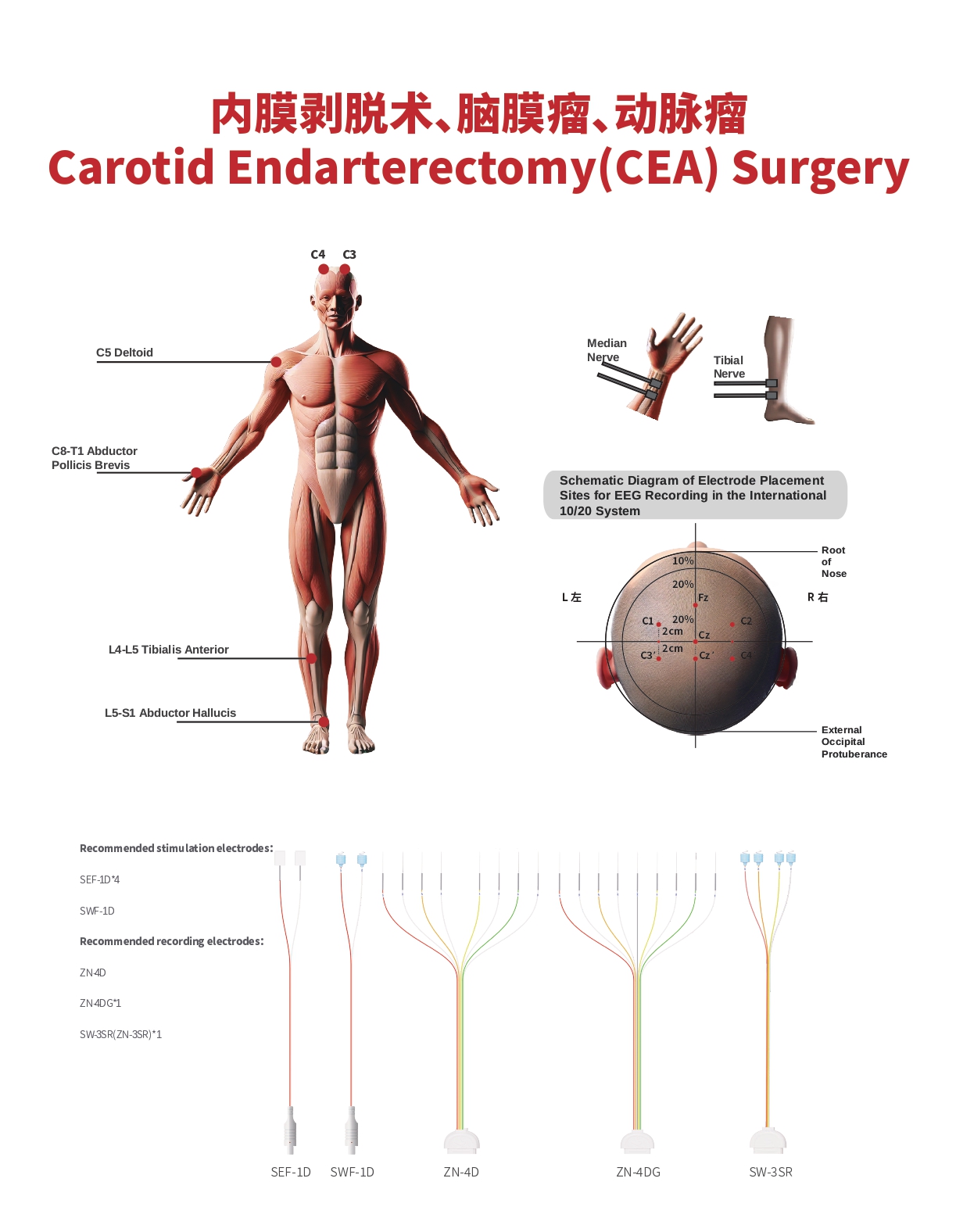
Somatosensory Evoked Potential (SSEP)
- Continuously monitors the sensory transmission pathway and can reliably reflect the perfusion status of the cerebral cortex.
Transcranial Electrical Motor Evoked Potential (TCeMEP)
- Assists in the diagnosis of cerebral ischemia.
Recommended Stimulation Electrodes:
- SEF-1D*2
- SWF-1D
- Recommended Recording Electrodes:
- ZN-4D*2
- ZN-4DG*1
- SW-3SR (ZN-3SR)*1
- Recommended Probe:
- XW220-II
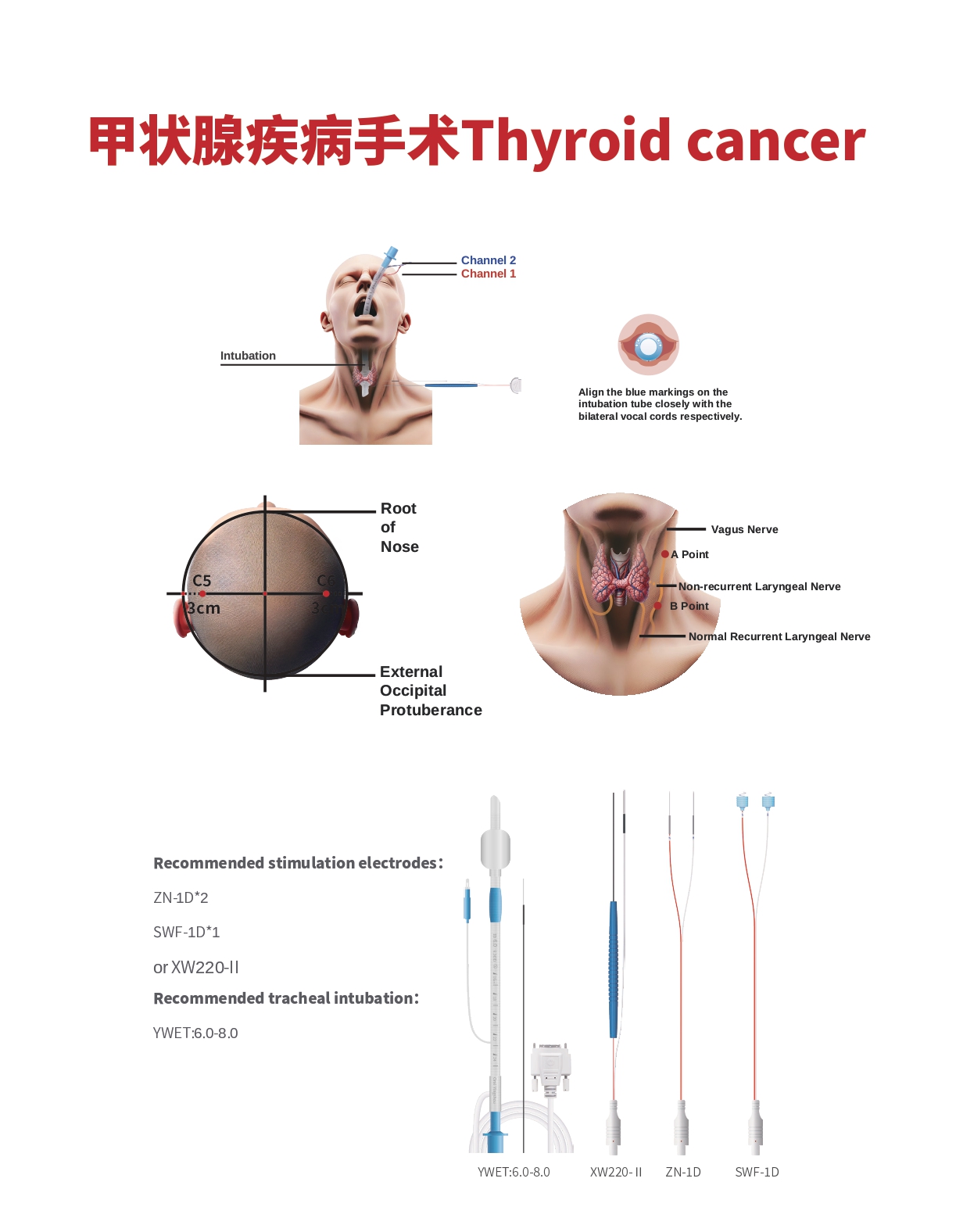
Free Electromyography (Free EMG)
- Monitors the traction responses of the recurrent laryngeal nerve and the vagus nerve.
Trigger Electromyography (Trigger EMG)
- Electrical stimulation of the recurrent laryngeal nerve or vagus nerve is used to locate the recurrent laryngeal nerve and vagus nerve, and to distinguish between normal recurrent laryngeal nerves and non-recurrent laryngeal nerves.
Motor Evoked Potential (MEP)
- Evaluates the postoperative function of the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
- Recording Site: Vocal cord muscles
- Stimulation Sites: C5 (3 cm above the ear), C6
Recommended Stimulation Electrodes:
- ZN-1D*2
- SWF-1D*1
- or XW220-II
- Recommended Intubation:
- YWET: 6.0-8.0
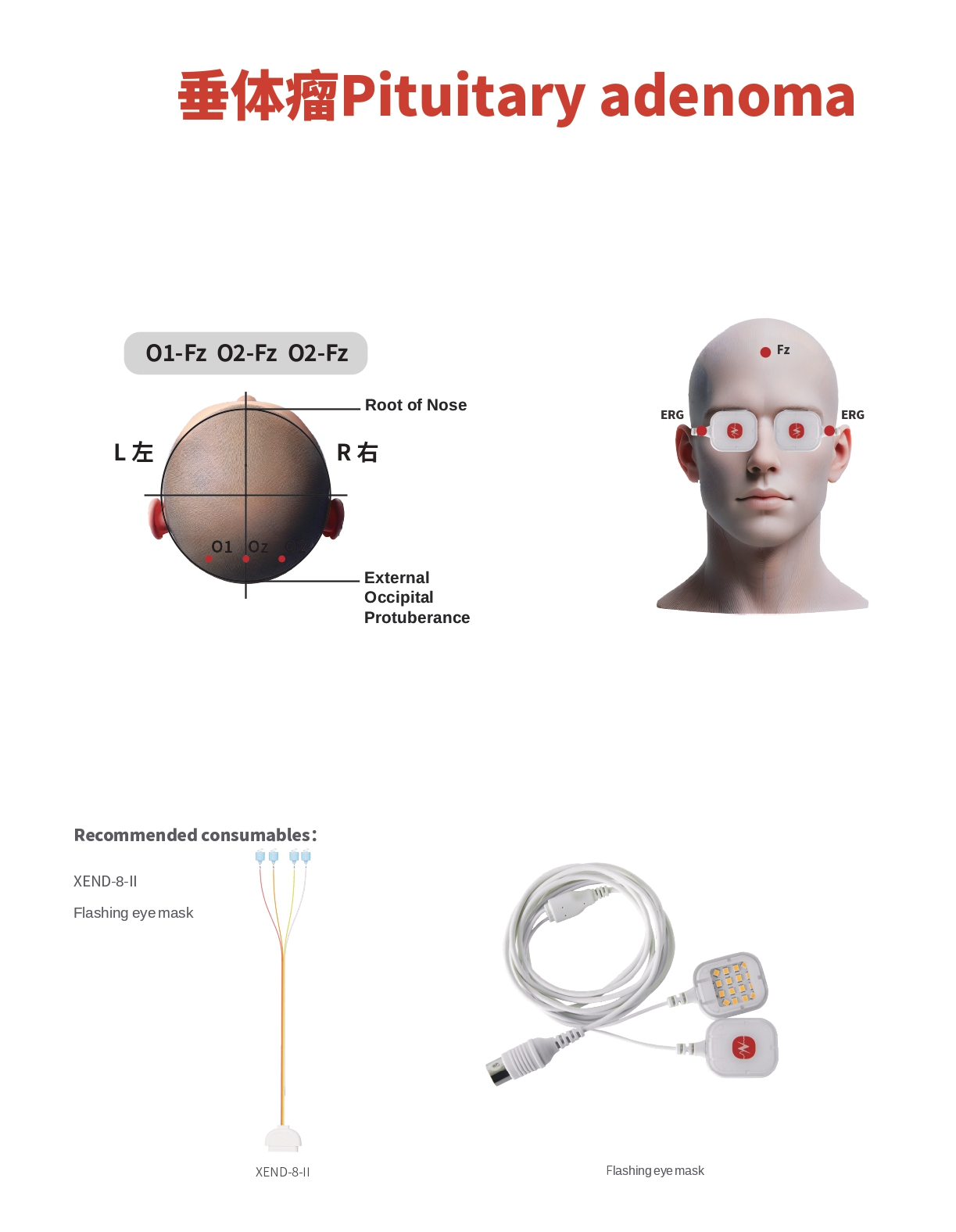
Visual Evoked Potential (VEP)
- Recording Sites:
- Recording electrodes are placed at:
- OZ (4 cm above the inion)
- O1 (4 cm to the left of OZ)
- O2 (4 cm to the right of OZ)
- Reference electrode is placed at Fz.
- Stimulation: Flash goggles
Recommended Consumables:
- XEND-8-II
- Flash goggles
FAQ
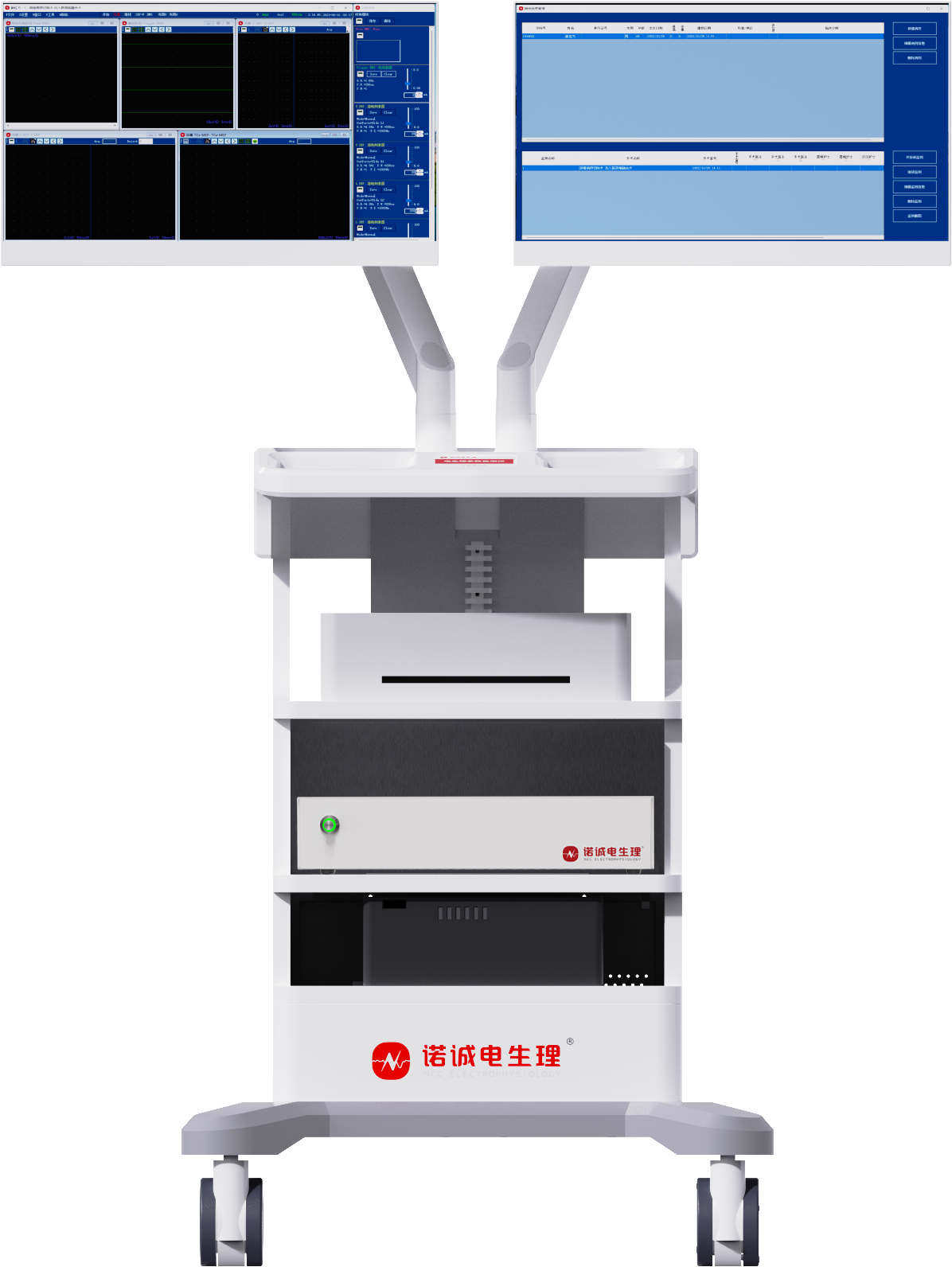
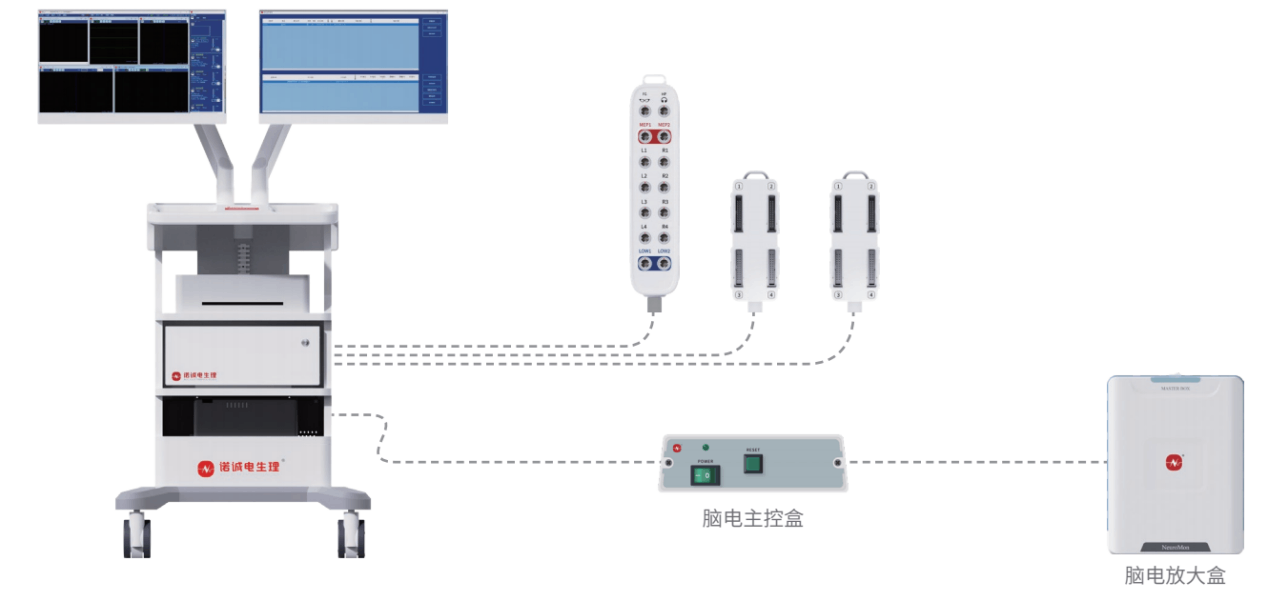
The intraoperative neurostimulation monitor developed by Nuocheng Electrophysiology is China's first intraoperative neuroelectrophysiological monitoring device applicable to complex surgical procedures and has obtained NMPA Class III medical device certification. The device provides monitoring of 32-channel IONM (Intraoperative NeuroMuscular Monitoring) + 256-channel EEG. It supports dual-screen adjustable display, with the main screen for real-time monitoring and the auxiliary screen synchronized with a microscope or video for convenient surgical operation.
The device has high-performance data acquisition capabilities, supports a portable design, and is equipped with all accessories for easy portability.
Figure: Intraoperative Neurostimulation Monitor (Dual-Screen)

Figure: Intraoperative Neurostimulation Monitor (Portable)
Supports multi-module monitoring, including SEP (Somatosensory Evoked Potential), MEP (Motor Evoked Potential), EMG (Electromyography), BCR (Bulbocavernosus Reflex), Motor Cortex Localization, Language Cortex Localization, EEG (Electroencephalography), BAEP (Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potential), VEP (Visual Evoked Potential), Blink Reflex, D-Wave, Pedicle Screw Monitoring, and other 16 monitoring modules.

It contains more than 20 templates for various surgical procedures, which can be personalized and saved as surgical templates according to monitoring needs.
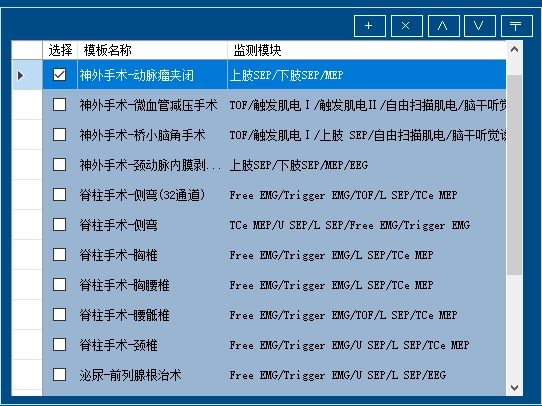
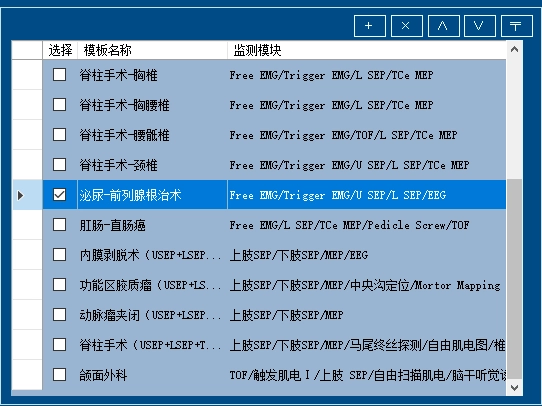
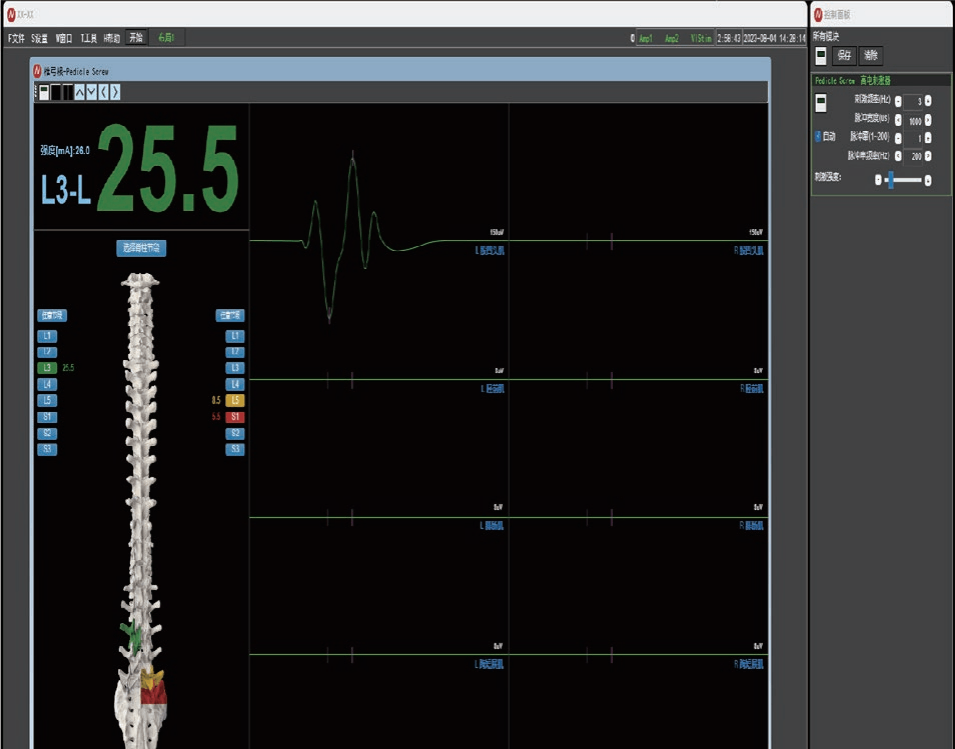
Automatically applies incremental pedicle probe currents. When the threshold is reached, the system stops intraoperatively without manual intervention, thereby monitoring whether the pedicle bone wall is breached and alerting the surgeon to avoid injuring adjacent nerve roots.
• The high-throughput signals from the 256-channel EEG provide a data foundation for brain-computer interface (BCI) development, while INOM verifies the accuracy of neural signal decoding in real time. Together, they enable breakthrough experiments such as "thought dialogue," accelerating the clinical translation of "brain-controlled" intelligent devices and postoperative rehabilitation.
• By integrating technologies, the precision of neurosurgical procedures is enhanced. In the future, combined with artificial intelligence, deeper breakthroughs are expected in the fields of precise epilepsy treatment, brain function protection, and personalized medicine.

Cross-regional real-time collaboration hub, global technology resource sharing ecology
• to establish the world's first open neuroelectrophysiological collaboration platform to support expert consultation between multinational medical institutions (for example, Australian experts provide expert advice to Indonesian surgeons remotely)
• to achieve the efficient allocation of experienced electrophysiologists resources and break geographical barriers and to establish a 24-hour expert support network
• Provide standardized neuromonitoring support to medically underserved areas, such as hospitals in remote, underdeveloped regions or island-based medical facilities
• junior operators can get real-time expert guidance through the system, reducing the dependence on highly experienced technicians
• The NeuGuard Central Neurological Monitoring System breaks through the traditional "one-to-one" monitoring mode, enabling a single technician to simultaneously and precisely manage multiple surgeries
• All-in-one design, easy operation
• The operation can be completed in one connection, greatly improving the efficiency.
• Guide the needle by color, intuitive and easy to understand, quick to use.
• Customized consumables combination, flexible adaptation
• Clinical-oriented consumable package design
• To meet the diversified needs of surgery, a special consumable package is provided for different surgical procedures.
• Strong anti-interference ability, accurate and reliable data
• Integrated consumables with excellent anti-interference performance, significantly improve the waveform fidelity.
• It provides more accurate and reliable monitoring data for surgery, and helps to ensure the safety and success of surgery.
NCC Rainbow electrodes-simplified operation, accurate monitoring, Safeguarding surgery!
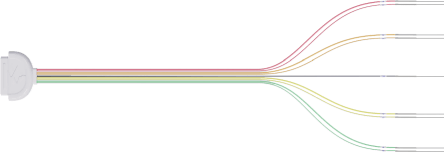
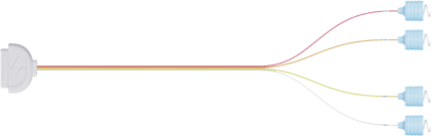
NCC Rainbow Electrodes
• Radiolucent Technology: Utilizes advanced carbon fiber material, which is invisible under DSA, reducing interference during surgery.
• Enhance Surgical Precision: Eliminate imaging interference, allowing surgeons to focus more on the surgical procedure and improving surgical success rates.
• Material Innovation: The application of carbon fiber material, which is lightweight and has high strength, provides stable support for surgery.
• Exceptional Performance: Stronger anti-interference capability and faster transmission rate ensure the stability and real-time performance of signals during surgery.

 中文
中文 Arabic
Arabic Spanish
Spanish Hindi
Hindi French
French Indonesian
Indonesian Portuguese
Portuguese Persian
Persian Russian
Russian Korean
Korean German
German Vietnamese
Vietnamese Turkish
Turkish