Understanding EEG Devices: How They Work and Their Applications
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a non-invasive technique used to measure and record electrical activity in the brain. EEG devices are essential tools in both clinical and research settings, providing insights into brain function, diagnosing neurological conditions, and facilitating brain-computer interface (BCI) technologies. At NCC, we are proud to offer advanced EEG solutions, including our Type-C, Type-D, and Type-F models, which are designed to meet the diverse needs of healthcare professionals and researchers. This article will explore how EEG devices work, their key features, and their various applications.
How EEG Devices Work
EEG devices operate by placing electrodes on the scalp to detect electrical signals produced by neuronal activity in the brain. These electrodes are typically arranged in a specific pattern, allowing for the recording of brain waves across different regions. The electrical signals are amplified and converted into digital data, which can then be analyzed to interpret brain activity.
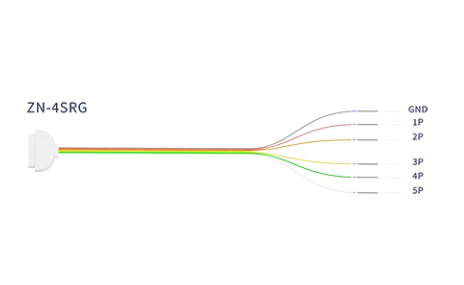
1. Electrode Placement: Electrodes are placed on the scalp according to the 10-20 system, a standardized method that ensures consistent and accurate placement for reliable data collection.
2. Signal Acquisition: The electrical signals detected by the electrodes are transmitted to an amplifier, which boosts the signal strength for better clarity and accuracy.
3. Data Processing: The amplified signals are processed using advanced software that filters out noise and artifacts, providing a clear representation of brain activity.
4. Visualization: The processed data is visualized in the form of waveforms on a monitor, allowing clinicians and researchers to analyze brain activity in real time.
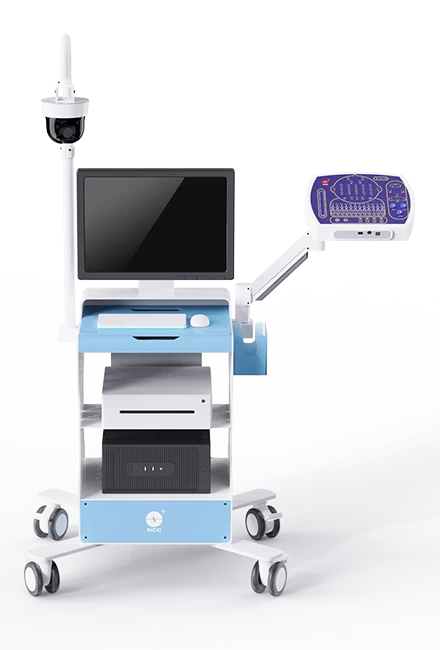
Key Features of NCC EEG Devices
At NCC, our EEG devices are designed with cutting-edge technology to ensure high-quality signal acquisition and user-friendly operation. Here are some key features of our models:
NCC Type-C EEG
- 20 Channels: Offers 19 channels for unipolar EEG and 1 for bipolar ECG, enabling comprehensive monitoring.
- Advanced Hardware and Software: Designed for high-quality EEG signal acquisition with built-in impedance testing.
- Bluetooth Connectivity: Allows for wireless data transmission, providing patients with freedom of movement during recordings.
- Long Battery Life: Supports up to 72 hours of recording with dry batteries, making it ideal for extended monitoring.
- Event Marking Button: Enables patients to mark significant events during dynamic recordings.
NCC Type-D EEG
- Versatile Channel Options: Available in 24, 36, 48, 60, or 72 channels for various applications.
- Optical Fiber Transmission: Ensures high-quality data transfer while eliminating AC interference.
- Integrated PSG Capabilities: Supports polysomnography (PSG) for comprehensive sleep studies.
- Ergonomic Design: Features user-friendly electrodes with DIN connectors for easy setup.
NCC Type-F Holter EEG
- Portable Design: Compact and lightweight, perfect for on-the-go monitoring.
- Real-Time Data Display: Wi-Fi connectivity allows for immediate visualization of EEG waveforms.
- Dynamic Recording: Equipped with a 16GB flash memory card for extensive data storage, supporting 4-5 days of continuous monitoring.
- Safety Features: Direct current operation minimizes the risk of electric shock and signal interference.
Applications of EEG Devices
EEG devices have a wide range of applications in both clinical and research settings:
1. Clinical Diagnosis: EEG is commonly used to diagnose conditions such as epilepsy, sleep disorders, and encephalopathies. It helps clinicians assess brain function and identify abnormal electrical activity.
2. Neurofeedback Therapy: EEG devices are utilized in neurofeedback therapy, where patients learn to self-regulate brain activity to improve mental health and cognitive function.
3. Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs): EEG technology is pivotal in developing BCIs, enabling communication and control for individuals with severe motor impairments.
4. Cognitive Research: Researchers use EEG devices to study cognitive processes, including attention, memory, and decision-making, providing insights into how the brain functions.
5. Sleep Studies: EEG is essential in sleep research, allowing for the monitoring of brain activity during different sleep stages and the assessment of sleep disorders.
6. Real-Time Monitoring: Portable EEG devices enable continuous monitoring of brain activity in various environments, including hospitals and home settings.
Conclusion
EEG devices are invaluable tools in the field of neuroscience, providing critical insights into brain function and enabling the diagnosis and treatment of neurological conditions. At NCC, we are dedicated to advancing EEG technology with our innovative devices, including the Type-C, Type-D, and Type-F models, designed to meet the diverse needs of healthcare providers and researchers.
For more information about our EEG devices and how they can enhance your practice or research, contact NCC today. Let us help you unlock the potential of brain monitoring with our cutting-edge EEG solutions.

 中文
中文 Arabic
Arabic Spanish
Spanish Hindi
Hindi French
French Indonesian
Indonesian Portuguese
Portuguese Persian
Persian Russian
Russian Korean
Korean German
German Vietnamese
Vietnamese Turkish
Turkish